Search engine optimization (SEO) experts eat keywords for breakfast, lunch, and dinner, and munch on them in between snacks—metaphorically speaking, of course—for the simple reason that keywords are one of the main tools of the trade. When someone types words or phrases into a search box and the search engine returns relevant results, that’s keywords at work!
Keywords range from single, standalone words to more complex key phrases that you place in your copy to drive organic search traffic to your website.
Simply put, keywords are words that people use in their web search whenever they’re looking for information, images, ideas, products, or services. Since you’re into SEO, you’ll want to target these keywords, which is why you may also think of them as your target keywords.
Apart from this definition, keywords have other identifiable qualities that can help you better understand their nature and how you should use them to drive business success.
In the context of SEO, keywords serve as some sort of directional signs that point search engines like Google to your website. When your website contains keywords that match what users are looking for, it’s a signal for search engines to show your brand name in the search results. This makes your website visible and accessible to internet users.
You could also look at keywords as content markers. Statistics say that the number of websites has reached the billionth mark, and that there are billions more of individual web pages. Based on these numbers, you can just imagine the amount of content that the internet holds. Through keywords, search engines have a way of telling which web pages from among the billions out there have the most useful or relevant answers for content searchers.
Keywords Are the Heart of Every SEO Strategy
The potential value of using target keywords to grow your business makes it imperative that you get keyword research and keyword mapping right from the get go. Remember that keywords give your business the online visibility that it needs in the digital marketing space. On the other hand, failing to optimize your website for search engines and end users through organic or unpaid search is nothing short of a missed opportunity to bring your brand closer to your target audience.
Since content is one of the criteria for ranking websites, you have to make your content understandable to Google and other search engines. And this can only be possible if you give proper context to your content by placing keywords into it. These keywords serve as clues for Google and company, telling them what your page or post is all about. Without this kind of understanding between search engines and your website, there’s simply no way that your brand or content will land on search results.
It’s worthy to note that you should be using keywords not only to get on Google’s radar but perhaps more importantly to attract customers to your website. When planning your keyword strategy, your goal should be to focus on the users or visitors of your site. Think about the words or language they’re using whenever they have something to find on the internet. Once you figure it out, you can decide on what keywords to target so that people using those search terms will find their way to your website.
It goes without saying that an ineffective keyword strategy will not be helpful for your business. There are a couple of ways this may happen:
- Using the wrong keywords. If you don’t know what keywords customers are using in their search, you might end up with the wrong keywords in your text. If this is the case, how will you be able to answer visitors’ queries or solve a problem they’re experiencing? Not getting the traffic you want or need for your site affects your search rankings and the chance for your business to earn revenue.
- Keyword stuffing. Keywords provide you with a means to gain website traffic as future customers use those words in their search queries. Once they land on your website, you then have an opportunity to show them more information about your business, product, or service. However, cramming your target keywords into a single piece of text results in Google penalizing you for keyword stuffing, since this doesn’t ruins the user experience. Just as you need to be careful in choosing your keywords, you also need to be mindful when and where to place your keywords.
Types of Keywords to Target
Keywords come in different forms, each of which serves a specific purpose. Keywords are categorized based on who or what they’re targeting as well as based on length.
Targeting keywords are phrases and terms that are geared toward your industry, business offerings, or audience. Targeting keywords include:
1. Market-defining keywords. These are keywords that your target audiences use when talking about your business or industry. Often, these terms will be broad and generic, but you can also define them into something more specific for your niche.
2. Customer-defining keywords. These are key phrases that relate to a specific subset of customers within a larger audience base. For example, someone might add the search phrase “for teenagers” to define the age bracket of the book shopper or reader.
3. Product keywords. These keywords contain specific descriptions about what you’re selling, such as brand or product name, type or model, and other relevant specifications.
4. Competitor keywords. These are keywords that competing businesses, products, or services use to attract their target market. Using competitor keywords gives you an opportunity to target a similar audience with the same interests or preferences.
5. Geo-targeted keywords. Geo-targeted keywords are tied to location-based searches. Searchers use these terms to find products or services that are near them or in other adjacent areas, so you’ll want to optimize your site for this type of keyword to boost your local rankings.
Types of Keywords by Length
The length of a keyword is generally tied to search volume, which pertains to how many searches are being made using those types of keywords.
There are three types of keywords in this category.
1. Short-tail. Also called head or generic keywords, short-tail keywords are often made up of one to two words only. Search terms using these keywords are rather broad but very popular among searchers, so the potential to get more traffic to your site is quite high. However, this means that the competition for this type of keyword is also high.
2. Mid-tail. These search terms are slightly more descriptive than short-tail keywords, since queries in this range may now be two to three words long. These keywords may be the perfect middle ground between short-tail and long-tail keywords since the search terms are more specific and attract a large search volume.
3. Long-tail. This type of keywords targets very specific searches, topics, or audiences understandably because searchers put in as many terms as they can to define their query.
Generally speaking, the longer the keywords, the lesser the search volume. However, this may prove to be helpful since there will be fewer pages trying to compete for ranking for this type of keyword. Moreover, you can get higher conversion rates from long-tail keywords since it logically follows that when you’re able to provide an answer to the most specific of searches, it means you’ve satisfied what the user exactly needs.
More About Keyword Types
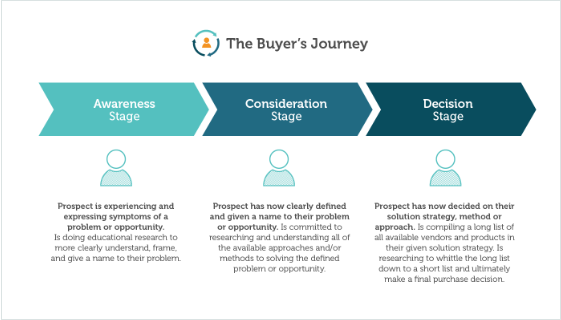
It’s worth mentioning that aside from matching the context of a search, Google also wants you to use keywords that match the users’ search intent. In order to use keywords effectively based on this criteria, you should track at which stage of the buyer journey your target audience is.
Someone who’s using informative keywords, for example, means that the customer is trying to know more about a certain topic or idea, so it will be impossible to attract this type of customer with keywords that relate to making a sale (also known as transactional keywords).
How to Use Keywords for SEO
The keyword research process involves identifying and filtering the list of search terms that you should be targeting. This is important, so you’ll be successful in ranking for a particular keyword.
Here’s what you need to include in your SEO strategy:
1. Create topic buckets.
At this stage, you can make a list of important and relevant topics surrounding your industry. Depending on the nature of your business, you could come up with 5 to 10 topic buckets, which you’ll be using to dictate your keyword selection as you go along
You might want to focus your buckets on the most popular topics or stories that are being talked about online or on topics that float around during your sales meetings.
Whatever topic buckets you choose, make sure they are subjects that interest and relate to your customers’ needs, while telling them what they need to know about your business.
2. Fill your buckets with topic ideas.
This is the part where you fill your content buckets with keywords that you think customers are including in their queries. Put yourself in the shoes of your customers and try to understand how they’re using the web to look for the information they need.
Use your buckets as a dump site of sort for all the keyword combinations you can think of, although you should be able to create a good balance of generic keywords that have a relatively low search volume and those that include more specific terms with higher traffic potential for your website.
3. Research related search terms.
When searchers are not quite happy with the search results they get, they are likely to scroll down to the bottom of the search engine results pages (SERPs) to see if there are searches related to what they were originally looking for. You can use these related search terms to come up with other ways with which users are phrasing their search.
4. Check competition.
Spying on your competitors’ SEO strategy gives you an opportunity to differentiate your brand from theirs, do more of what they’re doing, and get better results for your efforts.
The key is in evaluating the keywords that your competitors are using, without necessarily picking them up if they don’t matter to your business or to your audience.
Just like how you try to have a good mix of generic keywords and more specific search phrases, you should also be able to make wise choices between trying to rank for more competitive keywords versus targeting for terms that are more specific to your brand, product, or service.
5. Use keyword tools.
You’ve come up with a working list of keywords. The next step is to narrow it down using data-oriented tools for keyword research and planning. There’s a wide variety of free tools out there to help you generate keyword ideas, look for search patterns among users, analyze competition, measure keyword relevance, and so on. All of these SEO insights can be helpful as you decide where to focus your time, energy, and investment moving forward.
6. Plan your content.
At this point, you’re ready to execute your keyword strategy, which is why you should be building informative and educative content. The more content you produce, the more opportunities you have to include your target keywords, receive more exposure, and get a higher position in the SERPs. This also ensures that you’re able to avoid keyword stuffing since you’ll have several instead of a handful of pages to put your keywords into use.
A Holistic Approach to SEO Keywords
Keyword research is the discipline that lays down the foundation of SEO and content marketing. Although we can never overemphasize the significance of laying down a solid strategy in keyword research, we can tell you that a lot of it entails serving your target audience and delivering the best user experience.
You’ll want search engines to show your website the moment someone starts a web search. To hit this target, you have to know your audience, speak their language, and make connections with them as they journey through the buyer process.
At the same time, it’s about trying to rank for a good position by establishing your company’s relevance on Google and other search engines through the same customer-centric brand of using relevant and highly targeted keywords for SEO.
If you need help taking your SEO strategy to the next level, SEO Company will match you with an agency that fits your business’ unique needs. Inquire now!